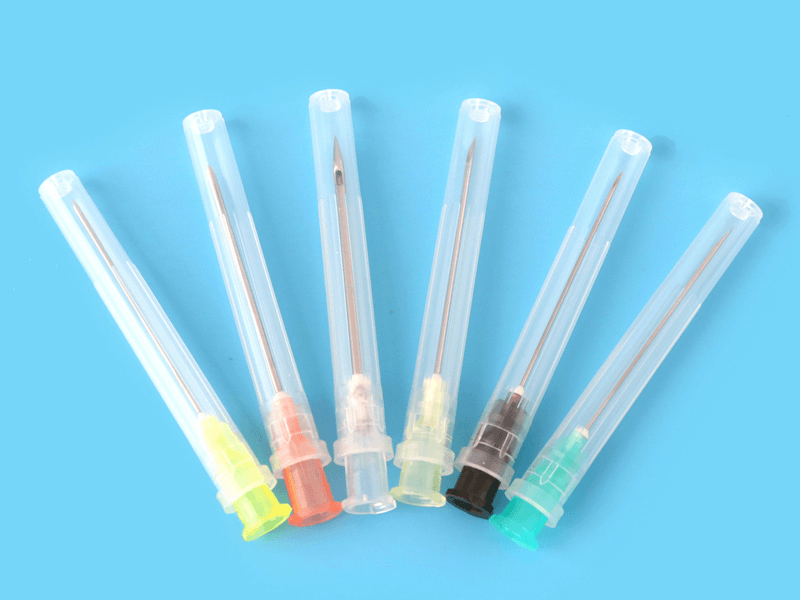
1. Introduction: The Foundation of Safe & Efficient Healthcare
In modern medical practice, high-quality Syringes and Injection Needles are the bedrock of patient safety and effective treatment. Far more than just simple medical consumables, they are the critical instruments behind every precise dosage and successful sample collection. For hospitals, clinics, and medical distributors, sourcing these essential hospital supplies is a challenging decision-making process that demands a perfect balance between clinical suitability, quality compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
This guide provides a comprehensive procurement framework to help decision-makers navigate everything from product types and quality standards to supply chain strategies, enabling you to make the most informed and responsible choice for your organization.
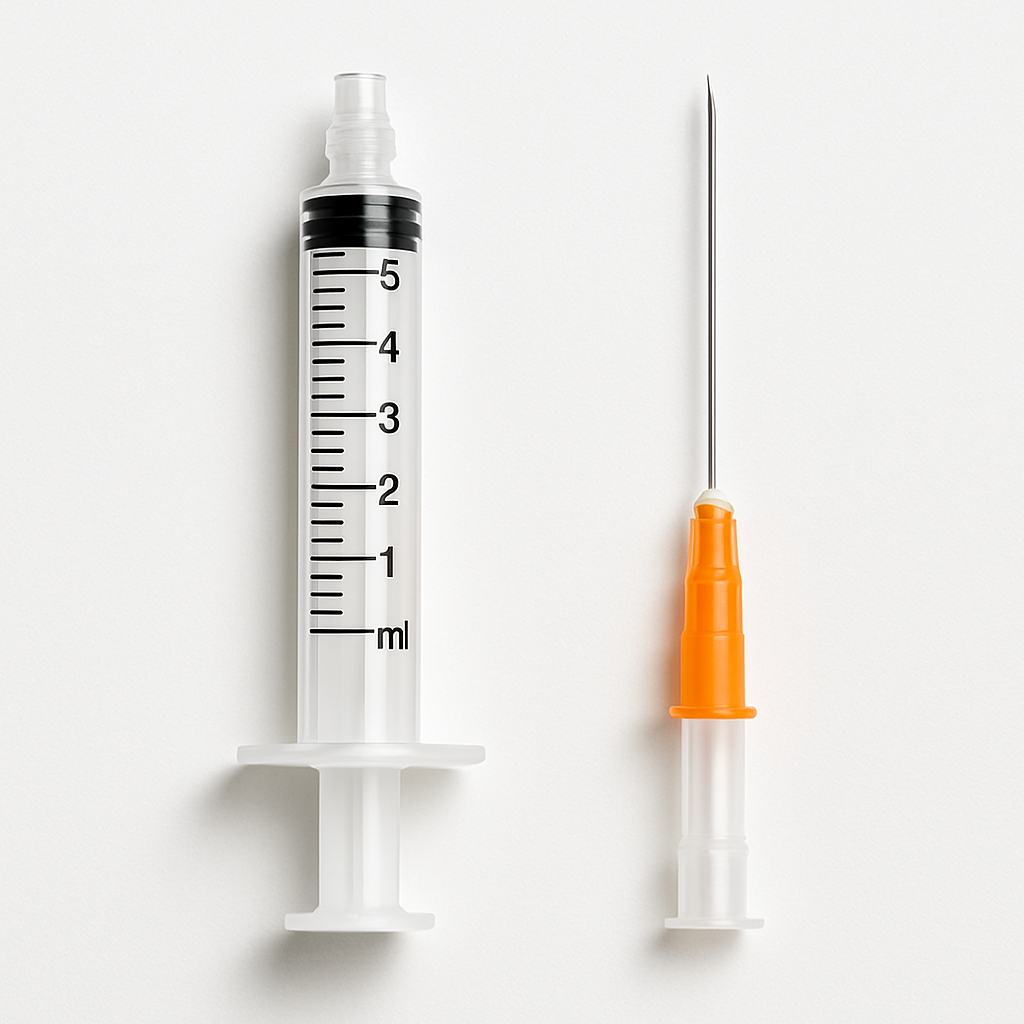
2. Deconstructing the Core Tools: A Detailed Guide to Syringe and Medical Needle Types
Matching the precise clinical need is the first step in procurement. Understanding the features, applications, and differences between various types of syringes and needles is fundamental to achieving precision medicine and operational safety.
2.1 Syringe Classification and Selection
- Luer Lock Syringe vs. Luer Slip: The Critical Difference in SafetySelecting the right tip connection directly impacts injection safety. The Luer Lock Syringe features a threaded design that allows a needle to be securely twisted onto the syringe tip. This provides superior connection stability, effectively preventing needle disengagement during high-pressure injections (like contrast agents) or over long-term infusions where pressure fluctuations or accidental tugs can occur.In contrast, the Luer Slip syringe relies on a friction-fit connection, offering faster operation for low-pressure, quick injections like standard subcutaneous or intramuscular shots. However, for any application demanding an absolutely secure connection, the Luer Lock design is the undisputed superior choice.
- The Necessity and Advantages of the Disposable SyringeIn today’s healthcare environment, using a Disposable Syringe (or single-use syringe) is the gold standard for preventing cross-contamination and eliminating the transmission of blood-borne diseases. Each individually sterilized syringe is designed for one-time use, fundamentally removing the risks associated with reuse.From an operational standpoint, while single-use products may seem to increase per-unit cost, they vastly improve workflow efficiency by eliminating complex cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization processes. More importantly, they significantly reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections and the severe medical incidents and high subsequent treatment costs they can cause, making them exceptionally cost-effective overall.
2.2 Precise Selection of the Medical Needle
- Selection by Injection Type: Intramuscular Injection Needle vs. Subcutaneous Injection NeedleMedication must be delivered to the correct tissue layer to be effective. Therefore, selecting the right Medical Needle based on the injection method is crucial.
- Intramuscular Injection Needle: Designed to deliver medication deep into the muscle. These needles are typically longer (e.g., 25mm-38mm or 1-1.5 inches) and have a moderate Gauge to effectively penetrate the skin and subcutaneous fat to reach the muscle tissue.
- Subcutaneous Injection Needle: Used to inject medication into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin, such as insulin or certain vaccines. These needles are generally shorter (e.g., 13mm-16mm or 1/2-5/8 inches) and finer (higher Gauge number) to reduce patient discomfort and ensure the medication remains in the correct layer.
- Understanding Hypodermic needle SpecificationsNeedle specifications are defined by both Gauge (G) and length. The Gauge determines the outer diameter of the needle shaft—the higher the number, the finer the needle. To help procurement managers get a clear picture, the table below lists common Gauges and their typical clinical uses:
| Gauge | Typical Color | Outer Diameter (mm) | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18G | Pink | 1.2 | Drawing up medication, viscous fluid injections, rapid infusions |
| 22G | Black | 0.7 | Most intramuscular injections, venipuncture |
| 25G | Orange | 0.5 | Subcutaneous injections (e.g., insulin), vaccinations |
| 27G | Grey | 0.4 | Fine subcutaneous injections (e.g., aesthetics, tuberculin tests) |
| 30G | Yellow | 0.3 | Local anesthesia, insulin pen needles |
3. Quality & Compliance: Ensuring Every Injection is Flawless
For B2B procurement, product quality certification and compliance are non-negotiable red lines. This is not just about regulations; it’s about your institution’s reputation and the lives of your patients.
3.1 The Importance of Certifications: Sourcing CE FDA Approved Syringe and Needle
Sourcing CE FDA Approved Syringe and Needle products is a critical step in ensuring they meet international market access standards.
- CE Marking: Indicates the product complies with the EU’s health, safety, and environmental protection regulations, serving as a passport for the European market.
- FDA Approval/Clearance: Signifies the product has been recognized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for sale and use in the United States market.
For any medical distributor or organization planning to sell products internationally, these certifications are mandatory requirements. For local healthcare facilities, choosing products with these certifications means the supplier adheres to stricter quality management systems and production standards.
“Choosing products with CE and FDA approval is not just a regulatory formality—it is a profound commitment to patient safety and institutional integrity.”
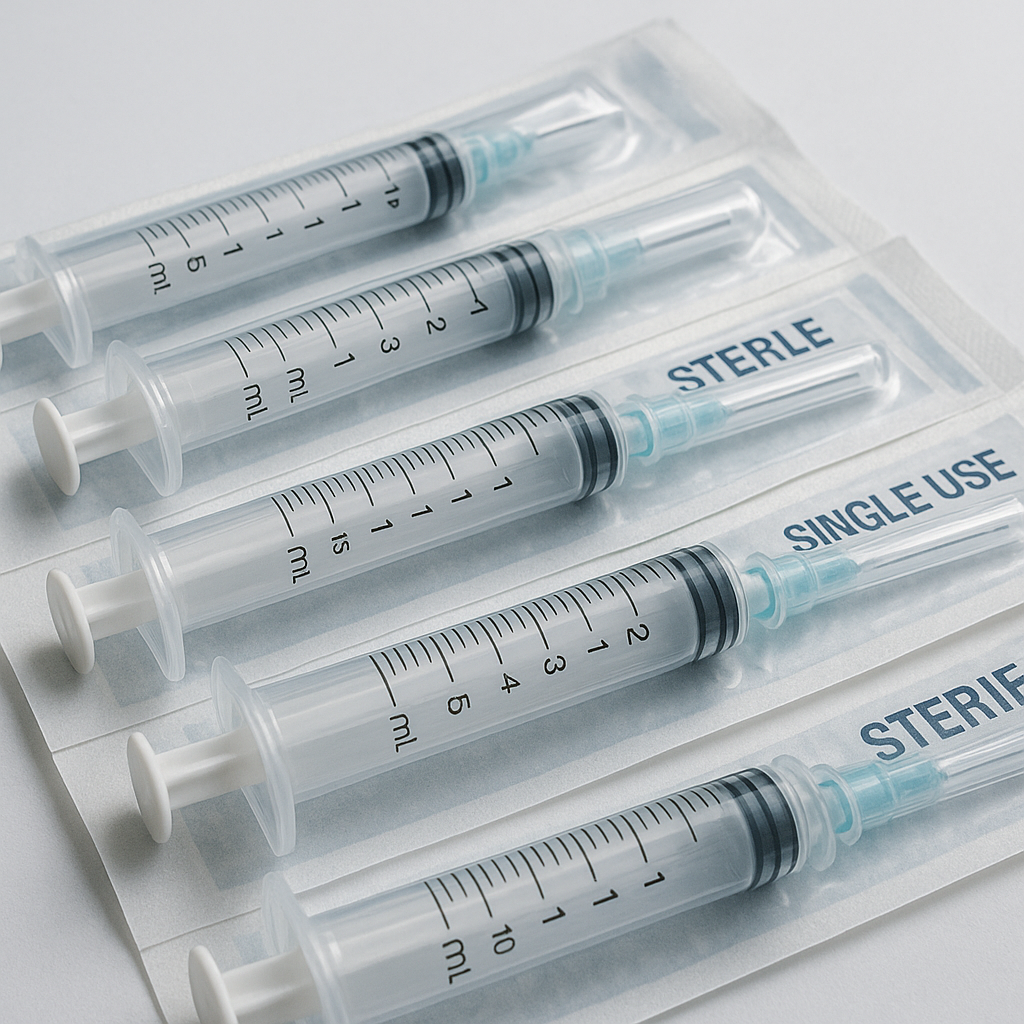
3.2 Production and Packaging of the Sterile Medical Syringe
A product’s sterile state is the core of its safety. A qualified Sterile Medical Syringe must not only undergo a strict sterilization process during manufacturing (e.g., Ethylene Oxide/EO sterilization), but its Sterilized packaging must also maintain its barrier integrity throughout transportation, storage, and distribution.
When procuring, carefully inspect the following:
- Individual Packaging: Each syringe and needle should be in its own sealed, intact package.
- Packaging Materials: Professional medical-grade dialysis paper and composite film should be used to ensure sterilizing agents can penetrate while effectively blocking microorganisms.
- Clear Labeling: The package must be clearly printed with the sterilization lot number, production date, and expiration date for traceability and inventory management.
4. Supply Chain & Partnership Models: Optimizing Your Procurement Strategy
Beyond the product itself, choosing the right supplier and partnership model is equally crucial for achieving an efficient and stable supply.
4.1 Ensuring a Stable Supply: Choosing a Reliable Medical Equipment Supplier
Partnering with an experienced and reputable Medical Equipment Supplier or medical distributor can deliver immense value. A reliable partner not only provides high-quality products but also ensures stable inventory, efficient logistics, and professional after-sales support, preventing clinical work from being interrupted by supply shortages. When evaluating suppliers, focus on their production capacity, historical delivery performance, quality control systems, and customer service level.
4.2 The Costs and Benefits of Bulk Syringe Supply
For high-volume hospitals or distributors, adopting a Bulk Syringe Supply model offers significant advantages. Bulk purchasing not only effectively reduces the per-unit procurement cost but also simplifies the purchasing process, cuts administrative overhead, and ensures the continuity of key hospital supplies. To maximize the benefits of bulk purchasing, it is advisable to build a scientific inventory management model based on historical usage data and future demand forecasts, thereby avoiding overstocking or shortages.

4.3 Exploring Customization: The Value of Partnering with an OEM Syringe Manufacturer
If you aim to build your own brand or have special requirements for product specifications and packaging, collaborating with an OEM Syringe Manufacturer is the ideal choice. The OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) model allows for deep customization based on your needs, such as printing your brand logo on products or packaging, creating specific kit combinations, or developing non-standard product specifications. This holds significant strategic value for medical distributors looking to establish a competitive edge and for large medical groups with unique clinical needs.

5. Conclusion: Make an Informed Choice to Fortify the Line of Medical Safety
In summary, selecting the right Syringe and Injection Needle is a strategic decision that requires a comprehensive assessment of clinical needs, quality compliance, cost-effectiveness, and supply chain management. A high-quality Disposable Syringe and Medical Needle are not just an expense; they are a critical investment in reducing medical risks, enhancing service efficiency, and safeguarding your institution’s professional reputation.
- To Hospitals and Clinics: Review your procurement standards today. Ensure the Syringes and Injection Needles you use meet the highest standards of safety and quality, providing a solid foundation for every medical procedure.
- To Distributors and Bulk Purchasers: Contact us to receive our full catalog of CE FDA Approved Syringe and Needle products and to discuss customized Bulk Syringe Supply solutions. Let us be your most trusted Medical Equipment Supplier as we contribute to the healthcare industry together.