Introduction to Infusion Sets: Your Lifeline for IV Therapy
Imagine this: You’re in a bustling ER, parched and weary, when a nurse swiftly connects a slender tube to your vein, delivering life-sustaining fluids in seconds. That’s IV therapy in action—over 90% of hospitalized patients rely on it, yet one mishandled setup could lead to complications like infections or air embolisms. Enter the infusion set, the unsung hero of hypodermic delivery systems, bridging IV bags to venous access protocols with precision.
But mastering infusion therapy basics isn’t just for pros; it’s vital for nurses, caregivers, and even empowered patients navigating home care. From selecting the right type—vented or non-vented—to ensuring sterile technique during priming and insertion, every step demands care to avoid pitfalls like blockages or phlebitis.
This guide demystifies IV administration, offering step-by-step insights into components, setup, monitoring, and troubleshooting. Unlock safe, confident use that safeguards health and streamlines care—your roadmap to flawless infusions starts here.
Why Infusion Sets Matter in Modern Healthcare
Hey there, friend—let’s chat about why these little tubes are such a big deal. In today’s fast-paced medical world, infusion sets are the backbone of IV therapy basics, making sure everything from hydration fluids to life-saving meds gets where it needs to go quickly and safely. Whether it’s rehydrating a dehydrated kid in the ER or delivering chemotherapy in a quiet oncology suite, these devices handle the heavy lifting. Without them, we’d be back to clunky, error-prone methods that could lead to uneven dosing or even infections. They’re precision tools that save time for nurses and peace of mind for patients, reducing risks like fluid overload symptoms or electrolyte imbalance in chronic disease IV management. In short, they’re not just gadgets—they’re gatekeepers of patient safety in everything from hospital settings to home health nurse routines.
Who Should Read This Guide: From Nurses to Curious Patients
If you’re a nurse brushing up on nursing IV administration or a caregiver diving into home care infusion therapy, this is for you. Even curious patients or family members learning about patient education IV therapy will find it super helpful. Whether you’re prepping for pediatric IV therapy, adult IV solutions, or elderly patient infusion care, we’ll cover it all in plain English. No jargon overload—just practical tips to make IV line care feel less intimidating and more empowering.
What You’ll Learn: A Roadmap to Safe and Effective Use
By the end, you’ll have the full scoop on infusion set usage, from unpacking the parts to troubleshooting IV complications like a pro. We’ll walk through IV setup instructions, flow rate adjustment, and even subcutaneous infusion for things like insulin pump infusion set care. Plus, we’ll touch on IV cannulation mistakes to avoid and signs of infection to watch for. Stick around—you’ll walk away ready to handle IV therapy tips with confidence!
What Exactly Is an Infusion Set? Demystifying the Basics
Okay, let’s break it down simply: An infusion set is that trusty tubing system that connects your IV bag to your vein, turning a bag of saline or meds into a steady stream of relief. It’s a sterile, single-use medical device designed for intravenous access maintenance, ensuring fluid administration or medication delivery systems work smoothly without drama.
The Role of Infusion Sets in Delivering Life-Saving Fluids
Picture this as the delivery service for your bloodstream. Infusion sets shine in IV therapy guide scenarios, shuttling everything from antibiotics to nutrients directly into the vein via continuous infusion or intermittent infusion. They’re essential for parenteral nutrition, blood transfusion sets, or even managing IV fluids at home. Without one, you’d risk uneven flow or contamination—yikes! In medical infusion procedures, they make sure venous access protocols are followed, preventing issues like adverse drug events IV and keeping the infusion process reliable.
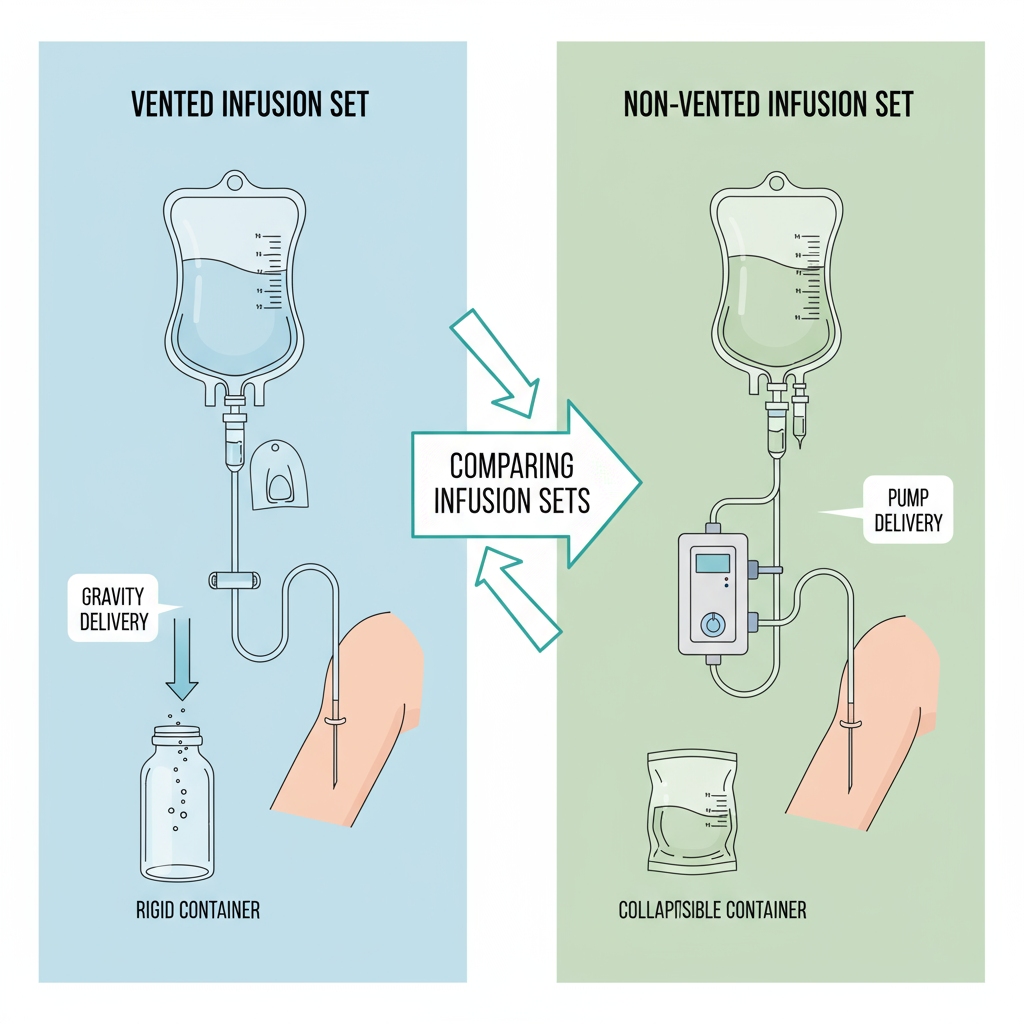
Types of Infusion Sets: Vented, Non-Vented, and Beyond
Not all infusion sets are created equal, folks. Vented ones have a little air vent for rigid bottles, letting air in so fluid flows out evenly—great for glass containers. Non-vented sets? They’re for flexible IV bags that collapse under pressure, no air needed. Then there are specialized types: macro-drip for big drops (faster flow), micro-drip for tiny ones (precise control), or even light-sensitive sets for photosensitive meds. For blood work, opt for a Blood Transfusion Set to handle those thicker fluids without clogging. Picking the right one? It depends on your IV fluid types and the therapy’s demands.
Benefits of Using Infusion Sets: Precision, Safety, and Ease
Why bother with these? Precision is key—they let you nail flow rate calculations for exact dosing, avoiding under- or over-delivery. Safety-wise, built-in features like filters guard against contaminants, cutting infection control for infusions risks. And ease? Nurses love how they streamline IV drip setup, freeing up time for patient care. Overall, they boost outcomes in everything from emergency medicine to long-term IV treatment guide scenarios, making therapy less stressful for everyone involved.
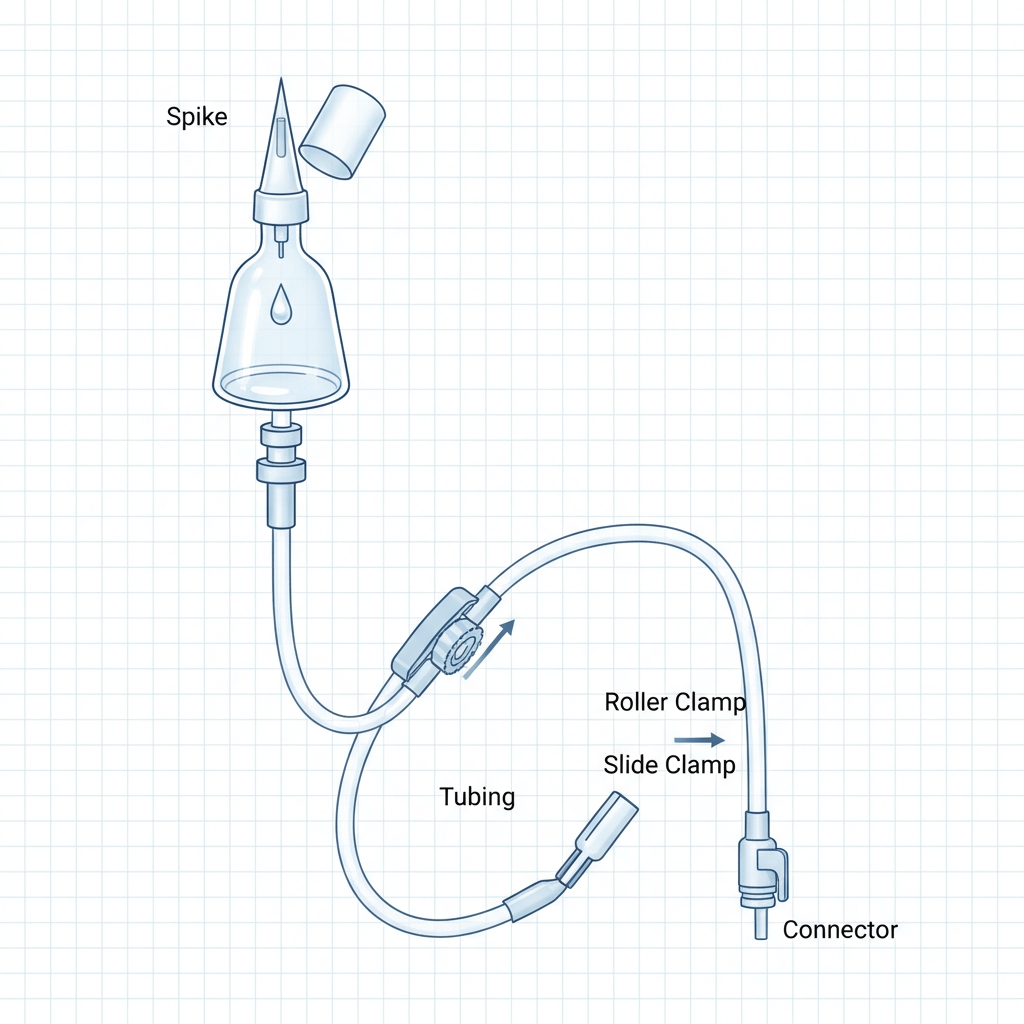
Inside the Infusion Set: Key Components Revealed
Ever wondered what’s inside that coiled tubing? Let’s unpack the infusion set components explained, piece by piece. Each part plays a role in safe IV line management, from entry to delivery.
The Spike: Your Gateway to the IV Bag
Meet the spike—it’s that sharp, pointy end that pokes into your IV bag‘s port. Made of sterile plastic or metal, it creates the fluid pathway without spilling a drop. Handle it carefully to keep that sterile technique infusion intact; one touch, and you’re risking contamination.
Drip Chamber Magic: Controlling Flow and Trapping Air
Ah, the drip chamber—your window into the action! This clear bubble lets you count drops for flow rate adjustment, typically aiming for 10-20 drops per minute depending on the set. It traps air bubbles (hello, air embolism prevention!) and often has a filter to snag particles. Squeeze it gently during priming to fill it halfway—voilà, smooth sailing.
Tubing and Clamps: The Flexible Backbone of Delivery
The tubing is the star here: long, kink-resistant PVC that carries fluids like a pro. Paired with the roller clamp, it lets you tweak the drip—roll it open for flow, closed to pause. Watch for tubing management issues like kinks; a quick straighten keeps things moving in IV fluid monitoring.
Filters and Ports: Guardians Against Contaminants and Add-Ons
Filters are unsung heroes, blocking bacteria or debris for cleaner delivery—think 0.22-micron wonders for total parenteral nutrition. Ports? Those Y-sites or injection ports let you add meds mid-flow without unhooking everything. They’re lifesavers for multi-drug regimens, but always scrub with alcohol first.
Connectors and Needles: Ensuring a Secure, Leak-Free Link
At the end, the Luer lock connector twists onto your catheter for a tight seal—no leaks, no worries. Needles or cannulas vary: winged infusion sets for tricky veins, or Scalp Vein Sets for peds. They ensure secure IV access devices, but remember, they’re single-use only.
Gear Up for Action: Preparing Your Infusion Set Like a Pro
Prep time is where the magic happens—or mishaps, if you’re not careful. Let’s gear up for infusion set insertion with IV setup instructions that prioritize safety.
Essential Supplies Checklist: Don’t Miss a Thing
Grab your kit: IV bag, infusion set, alcohol swabs, tourniquet, gloves, tape, and a sharps container. For extras, consider Safety Syringes with Retractable Needles to avoid needlesticks. Double-check expiration dates—nothing ruins a good setup like outdated gear.
Hand Hygiene and Patient Prep: Building a Sterile Foundation
Start with soap and water or sanitizer—sterile technique for IV is non-negotiable. Explain to your patient: “This’ll be quick, just a little pinch.” Clean their arm with antiseptic in circles, letting it dry fully. Position them comfy, maybe with a warm pack for vein dilation.
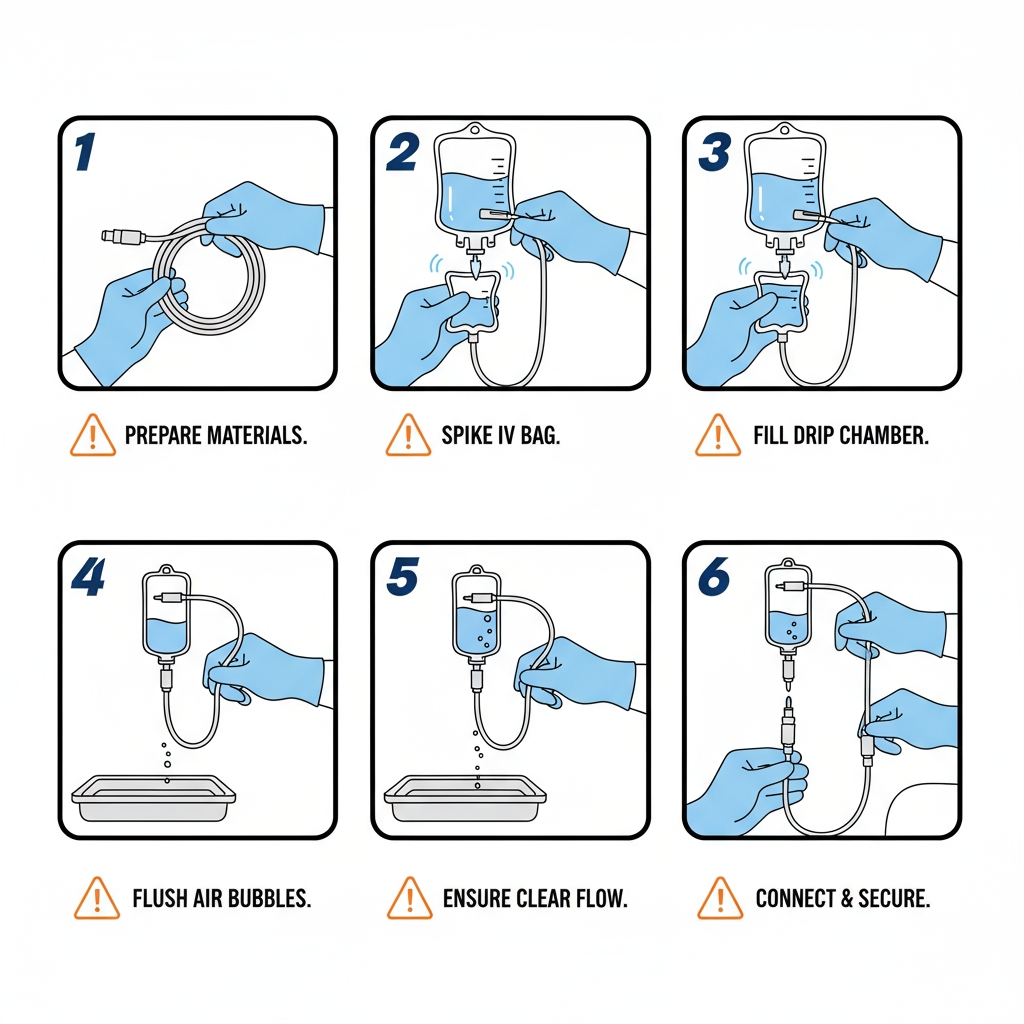
Priming the Line: Banishing Air Bubbles for Smooth Flow
Hang the bag high, close the clamp, spike the port, and squeeze the drip chamber half-full. Open the clamp over a sink—watch fluid chase those air bubbles out. Tap ports to dislodge stragglers. Priming IV tubing is your embolism shield; skip it, and you’re playing roulette.
Checking the IV Bag: Spotting Issues Before They Start
Inspect that bag: Clear fluid? No leaks or particles? Right label? Cloudy stuff means toss it—better safe than dealing with IV medication administration safety scares later.
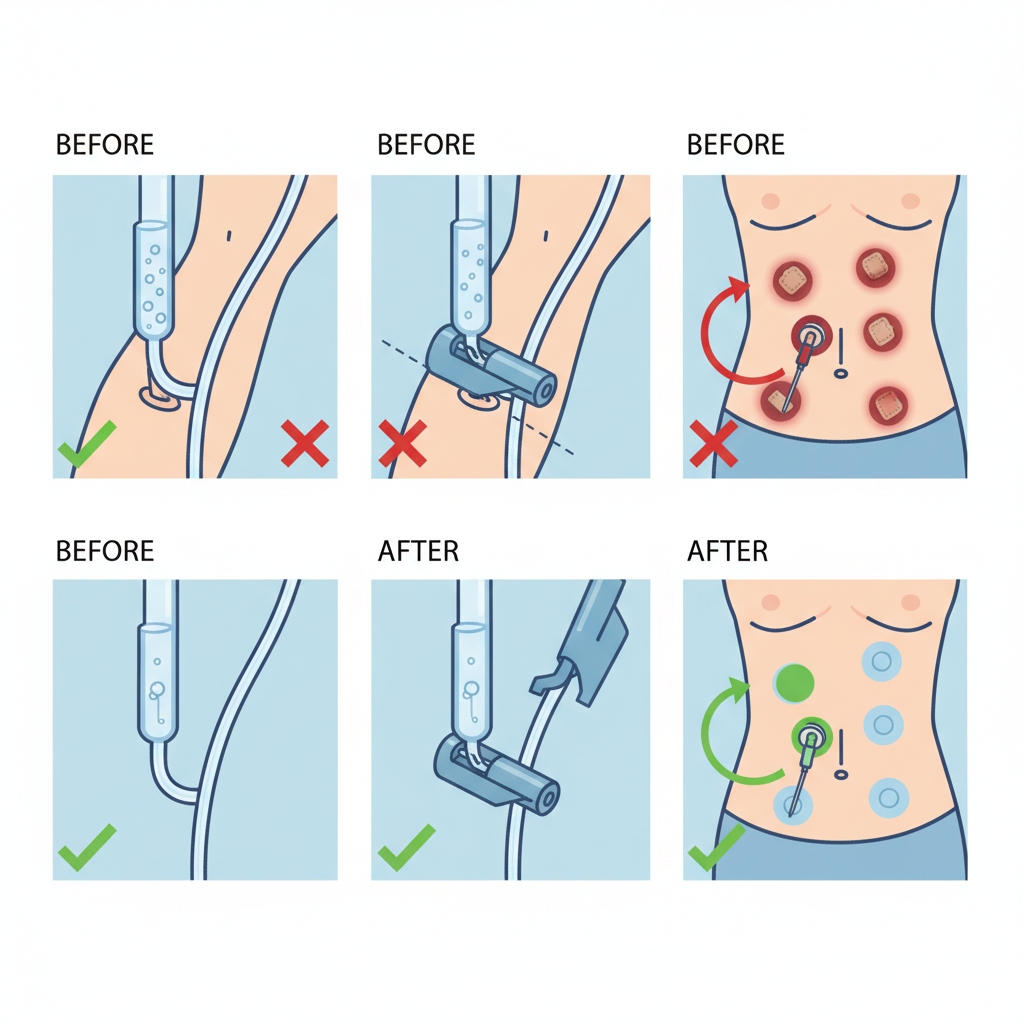
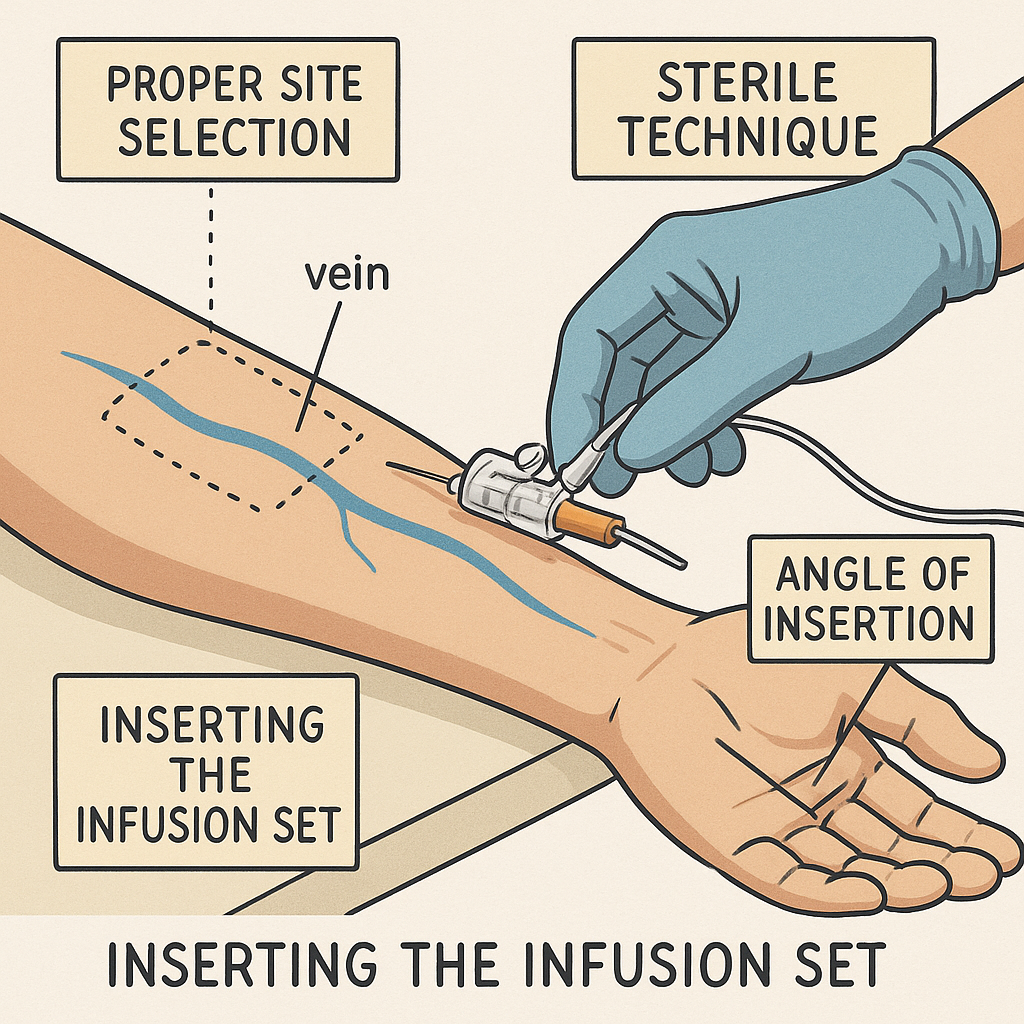
Site Selection Secrets: Picking the Perfect Vein
Go for the hand or forearm—avoid wrists or bends. Tap or fist-pump to pop veins; use a light if needed. Vein selection for IV follows cannulation best practices: straight, bouncy ones win. Rotate sites to prevent skin integrity issues.
Insertion Mastery: Step-by-Step to Flawless IV Placement
Insertion is the big moment—nail it with these steps for peripheral IV insertion. Remember, IV cannulation techniques demand steady hands and sterile equipment.
Stabilizing the Vein: Techniques for Easy Access
Tourniquet on, 4-6 inches above. Anchor the vein with your non-dominant hand, pulling skin taut. For tricky spots, try Scalp Vein Sets —they’re gentle for fragile veins.
- Clean the site with chlorhexidine.
- Stabilize and palpate.
The Art of the Angle: Inserting with Precision and Confidence
Bevel up, 15-30 degrees—shallow for surface veins. Advance until flashback (blood in the hub). Ease in the catheter, then withdraw the needle.
Flashback Confirmation: Knowing You’ve Hit the Vein
That blood flash? Gold star! It means you’re in. No flash? Reposition or try another site—don’t force it.
Securing the Catheter: Taping and Dressing for Stability
Advance catheter fully, remove needle to sharps. Connect tubing, flush with saline. Tape wings down, add transparent dressing. Secure IV catheter like a pro—no wiggles.
Flushing and Testing: Confirming Patency Right Away
Aspirate for blood return, then flush—no resistance? Pat on the back. This confirms IV access and clears any debris.
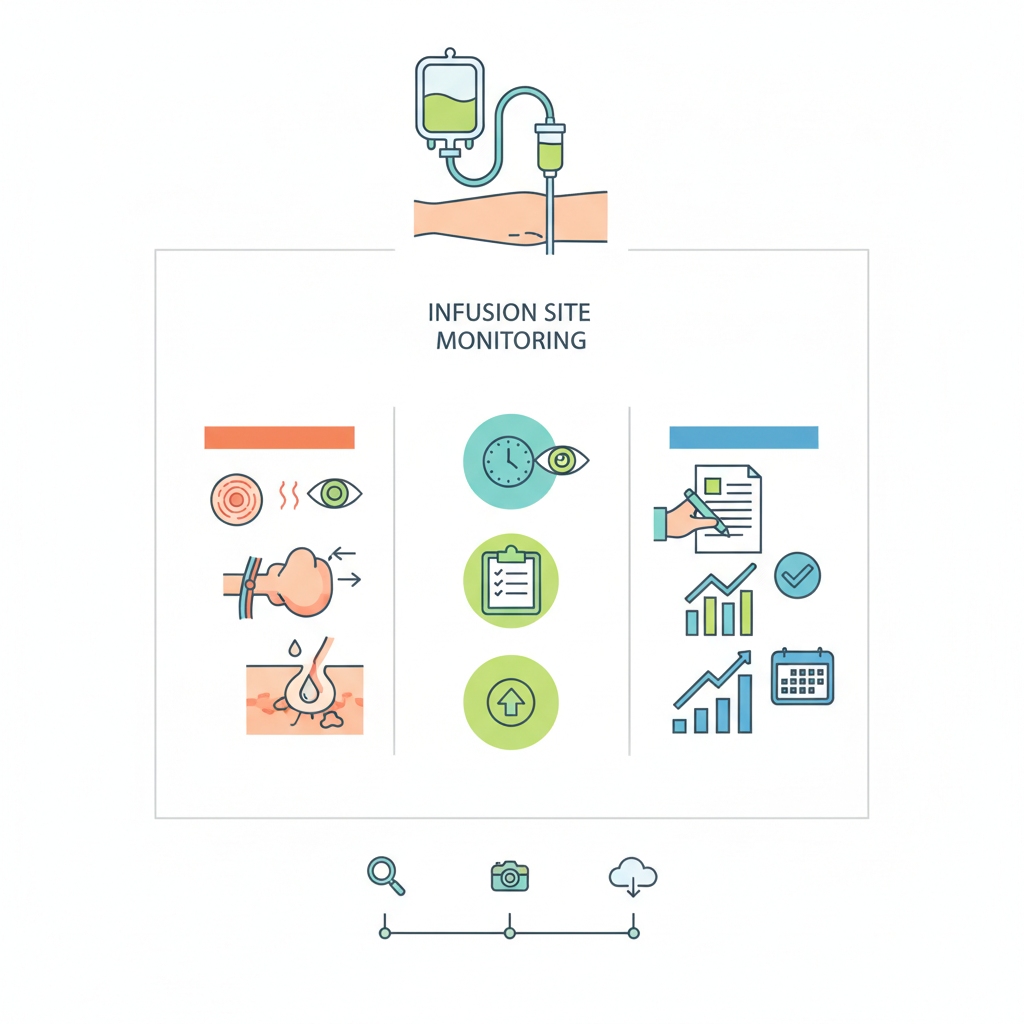
Vigilant Monitoring: Keeping Your Infusion Set on Track
Once it’s in, monitoring infusion set IV therapy is your watch duty. Catch issues early with IV site care routines.
Frequency Check: How Often to Inspect for Stability
Every 1-2 hours for high-risk patients; shift-end for stable ones. Check dressing, tubing, and flow—IV dressing change as needed.
Spotting Red Flags: Signs of Infiltration and Phlebitis
Swelling or cool skin? Infiltration—stop and remove. Red, hot vein? Phlebitis alert. For complications, consider Blood Purification options if needed.
Flow Rate Watch: Maintaining the Perfect Drip
Count drops or use a pump—adjust clamp for steady flow. Slow? Check kinks. Watch for IV pump troubleshooting alarms.
Patient Vital Signs: Beyond the Site to Overall Health
BP, pulse, respirations—fluid overload symptoms like edema? Slow it down. Holistic IV fluid monitoring saves lives.
Documentation Do’s: Tracking Every Detail for Safety
Note site condition, flow rate, patient response. Documentation of IV therapy is your legal lifeline—don’t skip it!
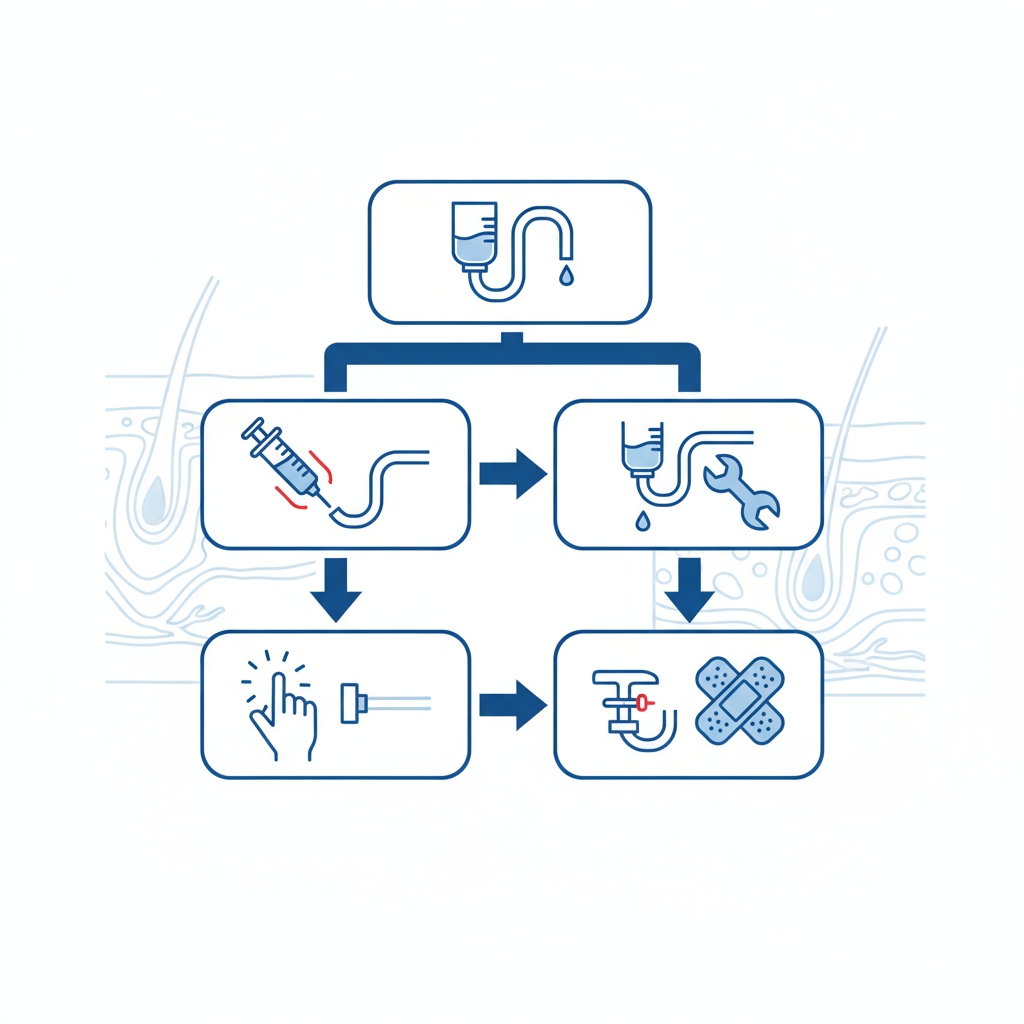
Troubleshooting Nightmares: Fixing Infusion Set Glitches Fast
Glitches happen—here’s your IV line troubleshooting toolkit for home care infusion set troubleshooting.
Air Bubble Busting: Quick Fixes to Clear the Line
Spot bubbles? Clamp above, tap to float them up. For big ones, syringe withdraw. Priming prevents most, but air in line? Act fast.
Blockage Battles: From Kinks to Clots, What to Do
Kink? Straighten. Clot? Gentle saline flush—no forcing! For dislodged IV catheter, re-site. Pump occlusion? Check all connections.
- Inspect tubing.
- Reposition arm.
- Flush if patent.
Pump Alarms and Slow Flows: Decoding the Warnings
Alarm blaring? Occlusion likely—trace the line. Battery failure? Swap or plug in. Programming infusion pump right avoids most woes.
Site Complications: Handling Swelling, Pain, and More
Pain or swelling? Stop infusion, elevate, compress. Phlebitis prevention starts with rotation. For infiltrated IV treatment, warm packs help.
When to Call for Backup: Knowing Your Limits
Unresolved blockage or fever? Dial your home health nurse or doc. Better safe—don’t play hero with IV therapy risks.
Safety Shields: Top Precautions to Prevent IV Disasters
Safety first, always! IV safety protocols keep everyone protected.
Aseptic Technique Essentials: Your First Line of Defense
Scrub hands, use sterile gear—aseptic non-touch technique is key. Clean ports before access to dodge bloodstream infections.
PPE and Hygiene Hacks: Protecting Yourself and the Patient
Gloves, masks if needed—PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) is your shield. Hand hygiene before and after? Non-negotiable for infection prevention infusion.
For extra caution, pair with Safety Syringes with Retractable Needles .
Medication Compatibility: Avoiding Dangerous Mix-Ups
Check labels— incompatible drugs cause precipitates. Flush lines between meds for safe IV medication administration safety.
Infection Prevention: CDC Guidelines You Can’t Ignore
CDC says: Replace sets every 72-96 hours, single-use only. Sharps disposal guidelines? Straight to the bin—no shortcuts.
Air Embolism Alerts: Why Priming Is Non-Negotiable
Air in? Deadly. Prime fully, secure connections—air embolism prevention saves lives.

Smooth Exit Strategy: Removing the Infusion Set Safely
Time to say goodbye? Do it right to avoid post-removal woes.
Timing It Right: When to Pull the Plug on IV Therapy
No longer needed? Remove ASAP—every 72-96 hours max, or at signs of trouble. Don’t leave it lingering.
Gentle Loosening: Minimizing Pain During Undressing
Peel tape slowly, use remover if sticky. Comfort your patient: “Deep breath—this’ll be quick.”
The Pull Technique: Steady Hands for Clean Removal
Gauze ready, pull parallel to skin—smooth and steady. No yanking!
Pressure and Inspection: Stopping Bleeds and Checking Integrity
Press 2-3 minutes; longer for bleeders. Check cannula—intact? Good. Dress and monitor.
Post-Removal Care: Watching for Delayed Complications
Watch for redness or swelling 48 hours. Hematoma? Cold compress. IV access devices done right means smooth recovery.
Pitfall Patrol: Common Mistakes and How to Sidestep Them
We’ve all been there—avoid these IV administration errors for smoother sails.
Overlooking Air Bubbles: A Recipe for Embolism Risk
Bubbles ignored? Embolism city. Prime every time—it’s your embolism shield.
Poor Site Choices: Why Rushing Leads to Failures
Rushed pick? Failures galore. Follow vein access tips: distal first, rotate often.
Ignoring Flow Rates: The Dangers of Unchecked Drips
Unmonitored drips? Overdose or underdose. Calculate and watch—flow control matters.
Skipping Documentation: Legal and Care Oversights
No notes? Chaos. Log everything for continuity and compliance.
Force-Flushing Fiascos: When to Stop and Resite
Pushing hard? Embolism risk skyrockets. Resistance? Resite—don’t force.
Elevating Your Practice: Best Practices and Pro Tips
Level up with these infusion therapy tips for pro-level care.
Vein Preservation Strategies: For Long-Term IV Success
Rotate sites, use smallest gauge—site rotation for insulin pumps prevents lipohypertrophy. Vein dilation tricks? Warmth works wonders.
Integrating Guidelines: INS, CDC, and Beyond
Follow INS for standards, CDC for infection control. Nursing guidelines IV administration? Your bible.
Patient Education Power: Empowering for Better Outcomes
Teach signs of infection, self-infusion guide basics. Empowered patients mean fewer calls.
Home vs. Hospital Use: Adapting for Different Settings
Home? Stock supplies, know emergency troubleshooting IV. Hospital? Team protocols shine. Adapt for diabetes care (insulin pumps) or clinic settings.
Future-Proofing: Innovations in Infusion Set Tech
Smart pumps with alarms, antimicrobial coatings—IV equipment maintenance evolves. Stay ahead for safer care.
Wrapping It Up: Mastering Infusion Sets for Lifelong Confidence
Whew, we’ve covered the gamut—from IV therapy basics to advanced tweaks. You’ve got this!
Key Takeaways: Your IV Therapy Cheat Sheet
- Prime always for air embolism prevention.
- Monitor sites hourly if high-risk.
- Document everything—safety first.
- Rotate for vein health.
When to Seek Expert Help: Red Flags You Can’t Ignore
Fever, severe pain, no flow? Call pros. Don’t DIY complications.
Resources for Deeper Dives: Books, Sites, and Training
Check INS standards, CDC site, or nursing IV procedures courses. Hands-on training? Gold.
Explore our medical supplies for safe IV care—stock up on quality infusion sets and more at Ary Medical today!

